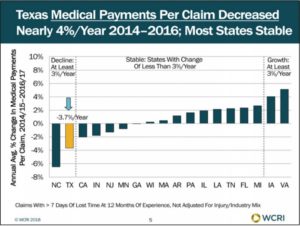
Medical payments per workers’ compensation claim in Texas decreased from 2014 to 2016 for claims with more than seven days of lost time, evaluated as of 2017. This followed several years of increasing medical costs, according to a recent study by the Workers Compensation Research Institute (WCRI).
“Payments for non-hospital care were the main driver of the recent decrease in Texas, with a decline in utilization of non-hospital (professional) services and little overall change in prices paid,” said Ramona Tanabe, WCRI’s executive vice president and counsel.
 The study, CompScope Medical Benchmarks for Texas, 19th Edition, examines medical payments per claim, prices, and utilization in Texas and compares them with 17 other states. The study also examines the longer-term trends to show how these metrics of medical payments and care have changed following the Texas series of reforms.
The study, CompScope Medical Benchmarks for Texas, 19th Edition, examines medical payments per claim, prices, and utilization in Texas and compares them with 17 other states. The study also examines the longer-term trends to show how these metrics of medical payments and care have changed following the Texas series of reforms.
“A series of reforms focused on medical costs, particularly House Bill (HB) 7 in 2005, impacted both prices and utilization of medical care as the various provisions were implemented beginning in late 2005 and continuing mainly through 2011,” said Tanabe.
The following are among the study’s findings:
- Medical payments per claim decreased nearly 4 percent per year in Texas from 2014 to 2016 for claims at 12 months of experience, but they were fairly stable in most study states.
- Prices paid for professional services grew rapidly after 2007 through 2011, reflecting fee schedule increases tied to Texas-specific conversion factors and Medicare updates. These prices were mostly stable from 2011 through 2017. Decreases in services per claim offset the increase in prices.
- Medical payments per claim were lower than the 18-state median for nonhospital and hospital providers in Texas.
To learn more about this study or to purchase a copy,visit https://www.wcrinet.org/reports/compscope-medical-benchmarks-for-texas-19th-edition.
Was this article valuable?
Here are more articles you may enjoy.

 Supreme Court Allows More Transport Workers to Bypass Arbitration and Sue Employers
Supreme Court Allows More Transport Workers to Bypass Arbitration and Sue Employers  Viewpoint: The Impact of Behavioral Health on Workers’ Comp
Viewpoint: The Impact of Behavioral Health on Workers’ Comp  Synopsys Sued by Private Equity Firm for Shopping $3 Billion Unit
Synopsys Sued by Private Equity Firm for Shopping $3 Billion Unit  Poll: Consumers OK with AI in P/C Insurance, but Not So Much for Claims and Underwriting
Poll: Consumers OK with AI in P/C Insurance, but Not So Much for Claims and Underwriting 